Blockchain Explained: A Beginner’s Guide to the Technology Shaping the Future
What is Blockchain, Really?
Blockchain is a disruptive technology that changes how people and organizations manage data and conduct transactions. Today, blockchain helps businesses record information securely without relying on a central authority.
Fortune Business Insights forecasts the global blockchain market to grow from $7.18 billion in 2022 to $163.83 billion by 2029.1 What’s behind this massive growth, much of which is expected in the financial services industry? Let’s take a look at what blockchain is, how it works and how data centers support it – a “101” approach, not a deep dive – to start answering that question.
Today, many industries use this technology to improve trust, reduce fraud, and speed up transactions. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global market is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. So, what makes it so powerful?
What Is Blockchain?
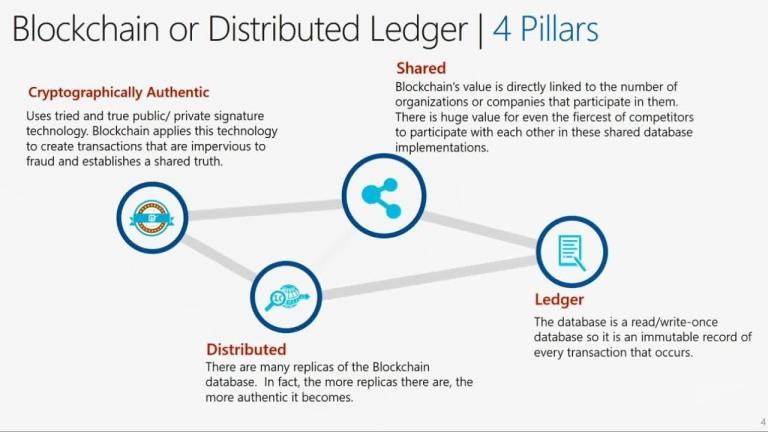
At its core, blockchain is software designed to record transactions and track assets. These assets can be physical, such as land or buildings, or digital, such as cryptocurrencies and intellectual property.
It is often called distributed ledger technology because it works like a shared accounting book. However, instead of being stored in one place, the data is copied across many computers in a network.
Two main features make this system unique:
-
Cryptography (strong encryption)
-
Decentralization (no single owner)
Because of this design, users can interact directly without needing a middleman like a bank.
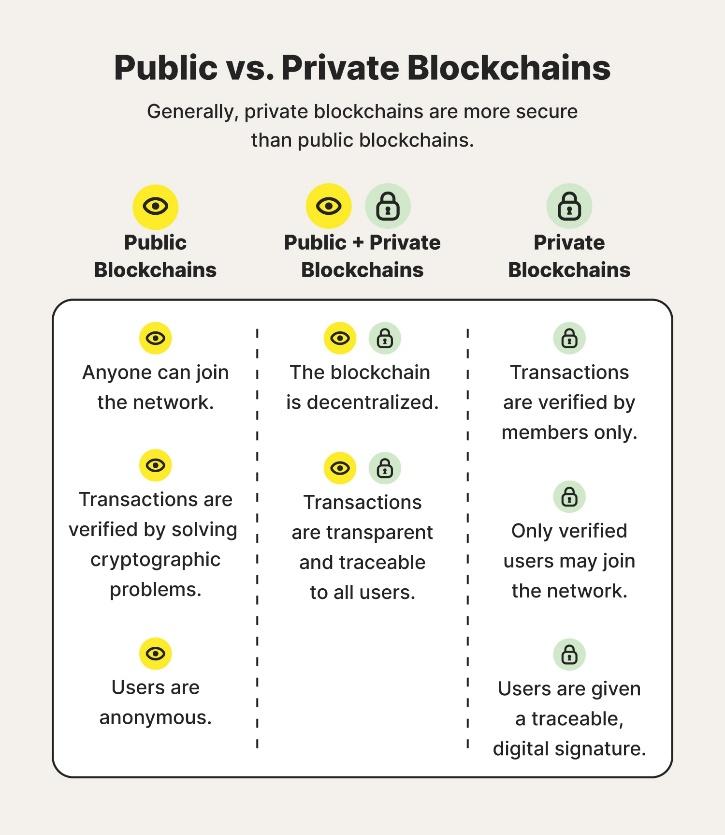
What Are Differences Between Public and Private Blockchains?
A peer-to-peer blockchain network (public or private) enables different blockchains to interact and allows authorized users to trade and track assets. In a simple model, computers of many users are connected through a single server, so data can move easily throughout the network.
How It Works?
As mentioned earlier, a blockchain consists of a series of recorded transactions, tracking the movement of assets, whether they are tangible like buildings or intangible like intellectual property. A transaction is recorded as an encrypted block of data. Common records cover who, what, when and where, but organizations can choose what data they want to record.
Each block records the time and order of transactions and, by design, blockchain prevents changes to data or to the sequence of blocks. The technology is considered immutable or incapable of change (no additions or deletions once a transaction is recorded on the ledger). However, when a new, authorized transaction occurs, a new block is added to the chain and the blockchain is updated in real time.
Why Invest in Blockchain?
Organizations invest in blockchain primarily to lower cost while improving efficiency. Examples of things that help them achieve this goal are immutability, which lessens the likelihood of fraud: one-and-done recording of transactions: and smart contracts as well as digital identities.
Resolving fraud cases is time-consuming and expensive. One-and-done recording takes far less time than typical duplicative accounting processes. A smart contract is software code that defines rules or conditions to automate executing what is set out in the contract. A simple example might be similar to a stop or stop-limit order on a stock trade – when the specified price is reached, the trade happens automatically. A more complex example is a supply chain; transactions involve multiple parties, prices, certifications, shipping terms and so on.
Blockchain proponents also believe that secure digital identities established in blockchain will streamline many processes and services that today rely on physical credentials such as social security cards, driver’s licenses and employment badges.
How Do Organizations Use Blockchain?
Blockdata research reveals that 65 of the top 100 public companies are actively developing blockchain technology, and more of the top 100 are in the research phase. According to Blockdata, the top use cases and high-level benefits are:
- Blockchain infrastructure services or blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) platforms that help other companies build blockchain technology through hosting or coding support
- Supply chain modernization to improve product tracking and other functions
- Clearing and settlement of financial assets between institutions to reduce cost and increase speed
Is It Secure?
This system is generally considered more secure than traditional databases. Because data is encrypted and distributed across many computers, it is difficult to alter.
However, it is not completely risk-free. Insider threats and credential theft can still occur.
Experts often say that an attacker would need to control more than half of the network to manipulate data. While possible, this scenario is unlikely in large networks.
How Do Data Centers Enable Blockchain?
Mining and validation processes require powerful hardware. Therefore, many organizations rely on specialized data centers.
These facilities provide:
-
Advanced cooling systems
-
High electrical capacity
-
Strong network infrastructure
In many cases, colocation centers are more cost-effective than building in-house systems.
Is Blockchain in Your Future?
Chances are, it is already part of your life. It may operate behind the scenes in supply chains, online payments, or even government systems.
Some industry groups predict that this technology will transform global trade, reduce fraud, and improve financial inclusion by 2030.
While these predictions remain to be seen, one thing is clear: digital transaction systems are evolving rapidly.
